As winter approaches and temperatures plummet, a reliable and energy-efficient heating system becomes necessary. With so many options available, selecting the right one for your needs can be confusing.
But fear not! In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the various types of home heating systems to help you make an informed decision and keep your home cozy all winter long.
From traditional forced air systems to innovative solar-powered solutions, a heating system suits every budget and preference. Read on to learn about the different types of heating systems and their unique benefits and drawbacks.
📘 Key Takeaways
- Forced air, natural gas/propane, electric, and radiant heating systems provide efficient climate control with varying installation processes and maintenance requirements.
- Heat pumps offer energy efficiency for both heating and cooling needs, while wood furnaces are an eco-friendly option.
- Consider cost, comfort, energy efficiency & home/climate when selecting a system. Seek professional help if needed.
⭐ Forced Air Heating Systems
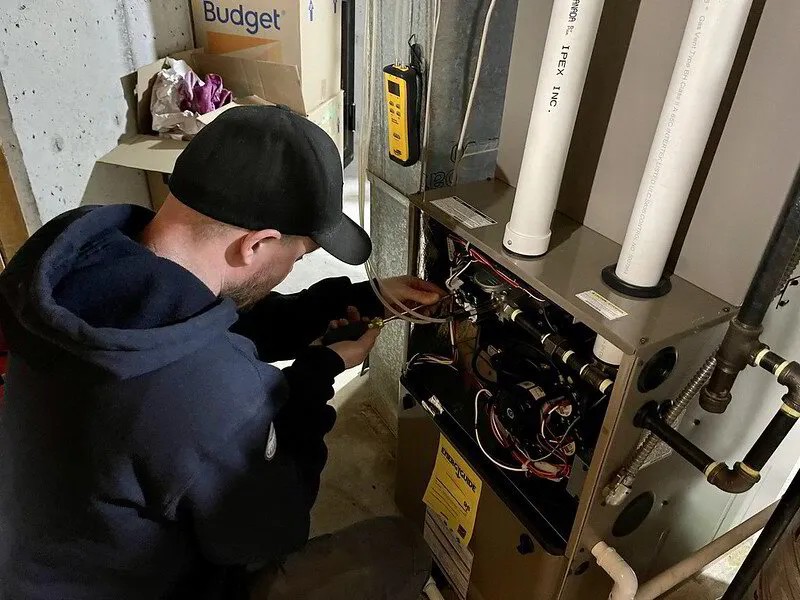
Forced air heating systems are North America's most common type of heating system, using a furnace and blower fan to distribute warm air through ducts.
They can be powered by natural gas, propane, or electricity and combined with air conditioning systems for year-round climate control.
One of the main benefits of forced air systems is their ability to evenly distribute warm air throughout your home evenly, providing consistent comfort. They also can incorporate indoor air quality systems, such as air purifiers and humidifiers.
However, there are some risks associated with forced-air heating systems, such as:
- the possibility of fires
- explosions
- gas leaks
- carbon monoxide poisoning
Mitigating these risks requires correct installation and regular maintenance. Combining a forced air heating system with central air conditioning allows for efficient year-round climate control, utilizing the ductwork for heating and cooling.
Natural Gas and Propane Forced Air Systems
Due to their energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness, natural gas and propane forced air systems are popular choices for homeowners. These systems can achieve efficiencies as high as 98.5% (AFUE or Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency).
However, they require a gas supply, which can pose risks such as gas leaks and carbon monoxide poisoning.
Installing a natural gas or propane-forced air system typically involves the following steps:
- Assessing the space
- Inspecting and adjusting the ductwork if necessary
- Connecting a gas line
- Ensuring proper ventilation
- Making electrical connections
- Testing and calibrating the system
Maintaining these systems regularly, including checks for gas leaks and proper ventilation, is necessary to ensure safety and efficiency.
Electric Forced Air Systems
Electric forced air systems offer an alternative to gas-powered systems, providing easy installation and maintenance.
These systems operate by:
- Drawing air into the system
- Passing it through a heat exchanger
- Warming the air with electric heating elements, creating heated air
- Circulating the warm air throughout your home
However, electric-forced air systems may have higher operating costs due to electricity usage.
To install an electric forced air system, you must adhere to codes and standards for air conditioning and ventilating systems, meet proper electrical requirements, install drain plugs as required in the drain pan, and provide adequate clearance and ventilation.
Annual electric forced air system maintenance includes cleaning the heating elements, checking thermostat settings, tightening electrical connections, lubricating moving parts, and regular inspections.
⭐ Radiant Heating Systems
Radiant heating systems offer a unique alternative to forced air systems, providing even and comfortable heat by warming surfaces rather than the air.
One popular option is floor radiant heating systems, which can be installed in floors, walls, or ceilings and powered by electricity or hot water.
One of the main advantages of radiant heating systems is their high efficiency. They utilize less energy overall and can be powered by renewable energy sources such as solar heating or geothermal heat pumps.
Radiant heating systems also benefit those with allergies or those impacted by dry air inhalation during winter, as they do not affect indoor air quality like forced air systems. Nonetheless, installation costs can be higher and repairs more complex.
Hydronic Radiant Floor Heating
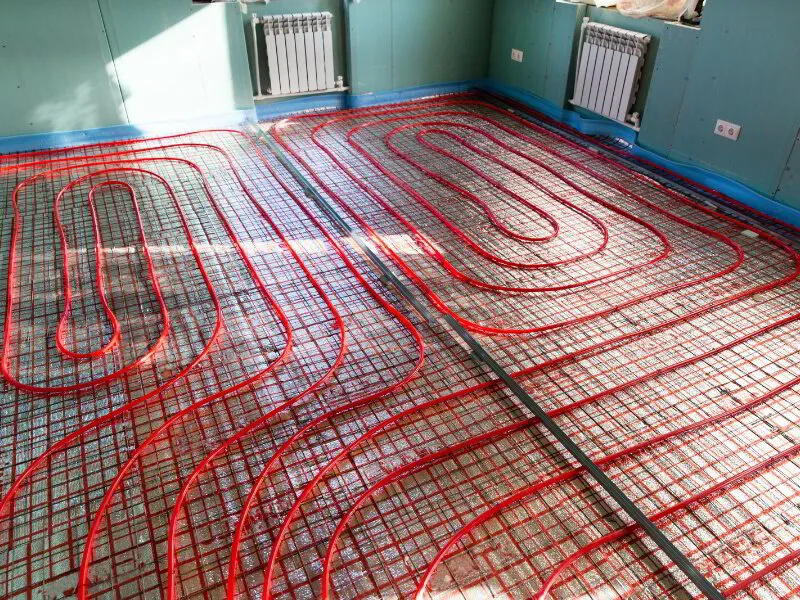
Hydronic radiant floor heating systems circulate heated water through pipes installed beneath the floor, providing energy efficiency and individual room temperature control.
These systems use EPDM rubber, PEX-AL-PEX, and PEX (cross-linked polyethylene) for the tubing.
The installation process of hydronic radiant floor heating involves the following steps:
- Designing the system according to the layout and heating requirements.
- Providing ample insulation to ensure efficient heat distribution.
- Drilling holes in the subfloor to accommodate the PEX tubing.
- Installing the tubing in a pattern.
- Securing the tubing in place.
- Connecting the tubing to a boiler or other heat source.
- Testing the system for leaks and proper functioning before covering it with flooring material.
Ceramic, porcelain, natural stone, tile, hardwood, luxury vinyl plank, laminate, and finished concrete are appropriate flooring materials for hydronic radiant floor heating systems.
Electric Radiant Floor Heating
Electric radiant floor heating systems use electric cables or mats beneath the floor, providing easy installation and lower upfront costs but higher operating costs than hydronic systems.
The components of an electric radiant floor heating system typically comprise electric heating cables or mats embedded in the floor, a thermostat to regulate the temperature, and a power source.
The installation process for electric radiant floor heating involves the following steps:
- Prepare the workspace by ensuring the subfloor is clean and level.
- Lay out the electric heating mats or cables according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Secure the heating element to the floor using hot glue or tape.
- Install a cement backer board over the heating element.
- Connect the heating element to the thermostat and electrical supply.
- Test the system to ensure it functions properly before installing the final flooring material.
Operational costs of an electric radiant floor heating system can vary depending on the heated area size and local electricity rates, with estimates ranging from $0.15 per hour to $0.22 per day.
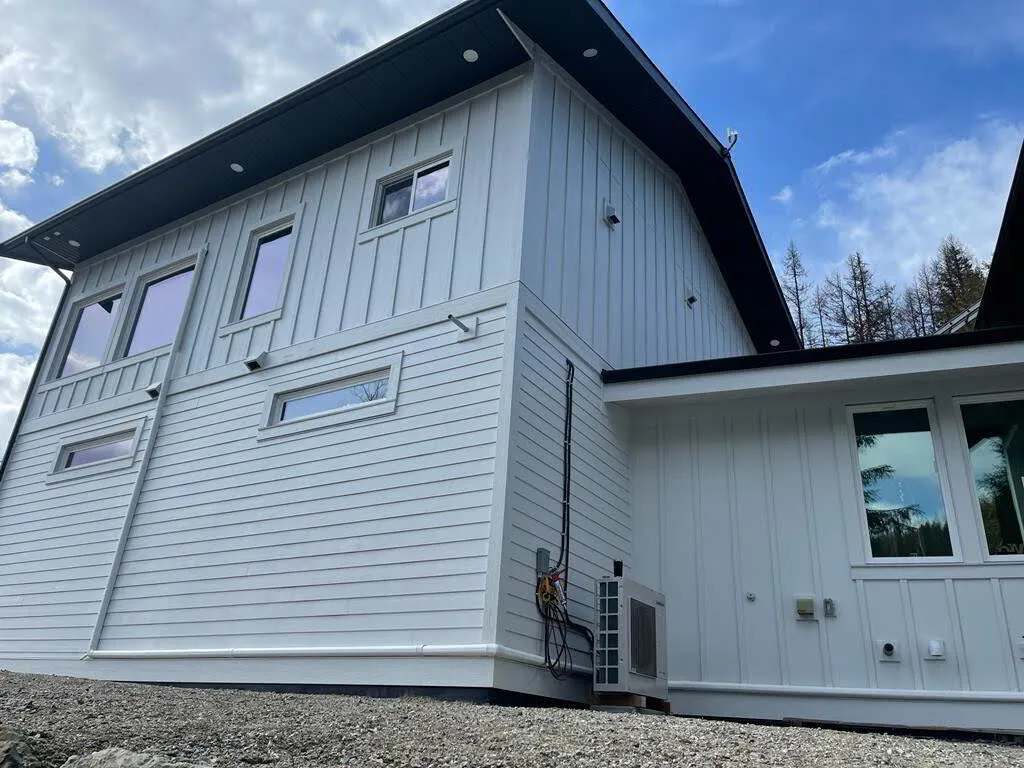
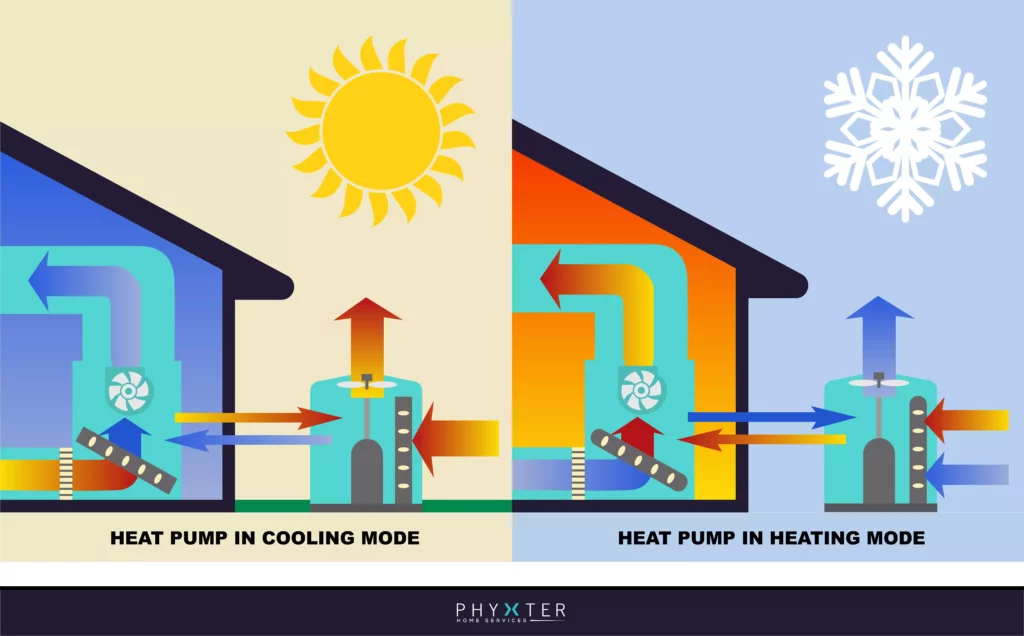
⭐ Heat Pump Systems
Image Courtesy of Phyxter Home Services
Heat pump systems are:
- Versatile and energy-efficient
- Provide both heating and cooling
- Transfer heat between the indoor and outdoor environments
- Typically powered by electricity, although natural gas models are also available
Heat pump systems are best suited for moderate climates and are less effective in extreme temperatures.
Several types of heat pumps are available, including air-source, ground-source, and water-source heat pumps. Each type has unique benefits and drawbacks, such as energy efficiency, installation costs, and maintenance requirements.
A consultation with an HVAC professional can guide you to the type of heat pump best suited to your home and climate.
📘 Related Reading: HVAC Insights: How Does a Heat Pump Work in Winter?
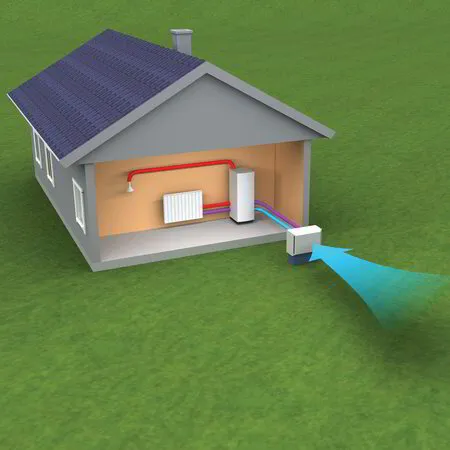
Air Source Heat Pumps
Air source heat pumps:
- Extract heat from the outdoor air
- Transfer heat indoors
- Offer efficient heating down to around 15°F (-9°C)
- Function by taking in heat from the ambient air
- Transfer heat into a building or space through a refrigeration system composed of a compressor and coils.
The principal components of an air source heat pump include:
- Compressor
- Fans
- Expansion valve
- Reversing valve
- Evaporator coil
- Condenser coil
Given their high efficiency, air-source heat pumps are an appealing choice for homeowners aiming to reduce energy consumption and heating costs.
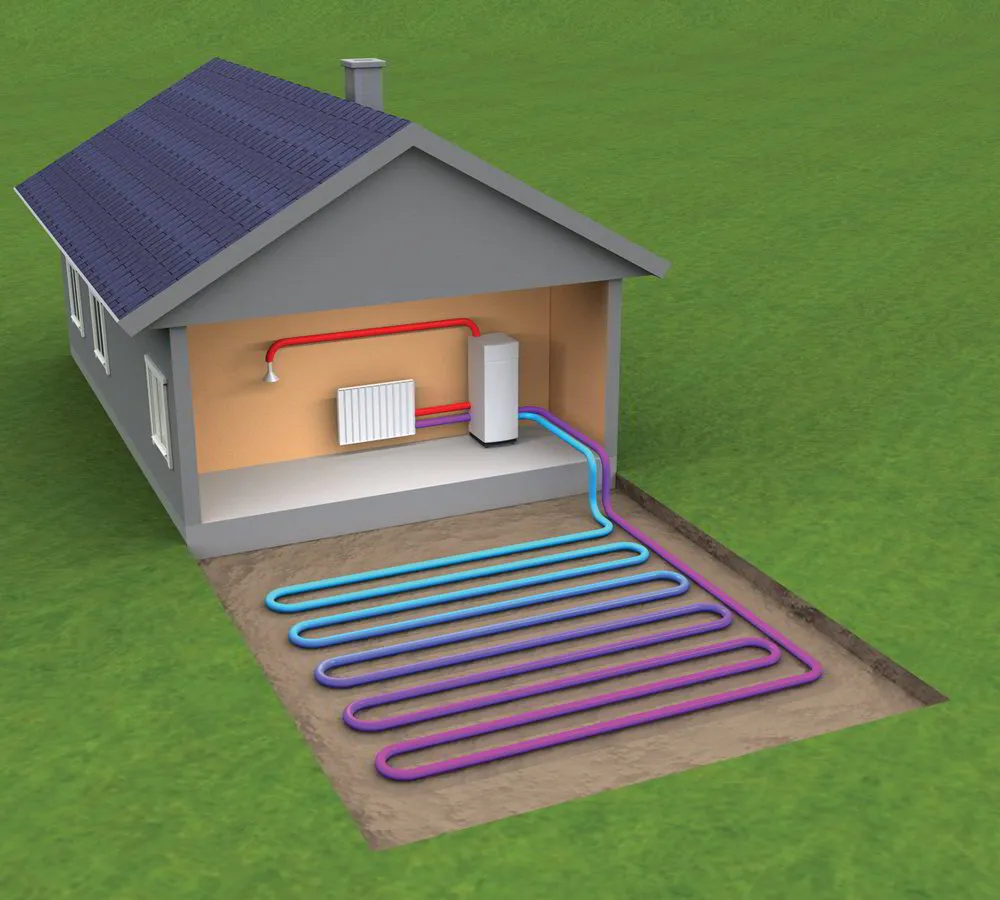
Ground Source Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps use the stable ground temperature to provide more consistent and efficient heating.
They employ a fluid, such as water or refrigerant, to circulate through underground pipes, absorbing heat from the ground and conveying it to a heat exchanger in the heat pump.
While ground source heat pumps are highly efficient, with the least efficient models exhibiting a 400% efficiency, they can be pretty expensive to install, with costs ranging from $10,000 to $38,000 for a 2,000 sq. ft. home.
However, their ongoing maintenance costs are typically low, ranging between $100 and $200 annually. The heat pump itself has a lifespan of 20 to 25 years, while the underground infrastructure may last for 25 to 50 years.
⭐ Boiler and Radiator Systems
Boiler and radiator systems use a central boiler to heat water or produce steam circulated through pipes to radiators or baseboard heaters.
These systems offer zoned heating and do not dry out the air like forced-air systems. Boiler and radiator systems combust natural gas, liquid propane, fuel oil, or electricity and are efficient ways to heat a building.
However, boiler and radiator systems may demand costly maintenance and a distinct cooling system for warmer months.
Overall, boiler and radiator systems can provide efficient and comfortable heating, but homeowners should carefully consider the costs and benefits before choosing this type of heating system.
Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are an older technology that heats water into pressurized steam, which is then distributed to radiators and returned to the boiler.
They can be powered by:
- natural gas
- liquid propane
- fuel oil
- electricity
Their efficiency ratings range from 80 to 88%.
Proper functioning of steam boilers necessitates regular maintenance, which includes:
- Performing bottom blow down and water column blow down
- Monitoring water quality
- Maintaining adequate water treatment processes
- Verifying the operation of the low water cut-off
- Cleaning the fireside of the boiler tubes.
Modern steam boilers can attain efficiencies as high as the mid-nineties, making them an energy-efficient option for homeowners.
Hot Water Boilers
Hot water boilers use pumps to circulate heated water to various heating systems, offering more precise temperature control.
They can be powered by:
- Natural Gas
- Liquid Propane
- Fuel Oil
- Electricity
Their efficiency ratings range from 80 to 88%.
The installation process for hot water boilers involves connecting the boiler to a central heating system, such as radiators or baseboard heaters, and ensuring proper ventilation and exhaust.
Hot water baseboard heaters range from $200 to $400, making them an affordable option for homeowners.
⭐ Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Ductless mini-split systems are:
- Modern electric heating and cooling systems
- Do not require ductwork
- Energy-efficient and easy to maintain
A popular choice for homeowners looking for a versatile heating and cooling solution. However, they may require multiple units for larger homes, which can increase the overall installation and maintenance cost.
These systems utilize a small outdoor compressor unit and indoor air handlers that can be situated in separate rooms throughout the house.
Hiring a professional for the installation will guarantee your system is energy-efficient and performs at its best. To ensure this, the technician will determine the best locations for the units based on the layout of your home.
Not only that, proper installation will decrease the chance of future operational issues, overall increasing the longevity of your system. Selecting the right HVAC professional for your mini-split AC installation can maximize the benefits of your ductless mini-split system.
With their high efficiency and precise temperature control, ductless mini-split air conditioner systems are an excellent option for homeowners looking for a modern, cost-effective heating solution.
⭐ Electric Resistance Heating
Electric resistance heating is an affordable and convenient supplemental heating option. It uses electric space heaters, such as portable space heaters or baseboard heaters, to provide targeted warmth in specific rooms.
These systems can also be used as a temporary heating solution in areas where a primary heating system is unavailable or requires repair. However, due to their relatively high electricity costs, electric-resistance heating systems are not typically used as primary home heating systems.
While they can provide supplemental warmth in specific areas, they may not be the most efficient option for heating an entire home.
⭐ Active Solar Heating Systems
Active solar heating systems use solar panels to capture and convert solar energy into heat, which can be used to warm a home.
They are eco-friendly, reducing reliance on fossil fuels for heating. However, they may require a backup heating system in colder climates or during periods of reduced sunlight.
These systems harness and distribute solar heat using collectors, a distribution system, a storage device, piping, pumps, valves, an expansion tank, and a heat exchanger.
Active solar heating systems can provide heat in multiple ways. This includes radiant floor systems, hot water baseboards, and central forced-air systems.
⭐ Hybrid Heating Systems
Hybrid heating systems:
- Combine the efficiency of heat pumps with the power of gas furnaces
- Automatically switch between the two as needed
- Suitable for extreme temperatures
- Provide consistent and efficient heating throughout the home
- Require regular maintenance for optimal performance and safety
Using a furnace or oil burner as a supplementary option, hybrid heating systems can offer reliable heating in colder climates where heat pumps may not be as effective.
This combination of heating technologies can help homeowners save on energy costs and reduce their environmental impact.
⭐ Wood Heating Options
Wood heating options are a renewable and cost-effective heating source, offering a cozy and traditional warmth for your home.
These options include:
- Wood furnaces
- Boilers
- Stoves
- Pellet stoves
Each option has its advantages and drawbacks.
Pellet stoves, particularly, are an eco-friendly option due to their clean-burning properties and construction from recycled materials. Wood heating options may be perfect for your home if you want a sustainable and cost-effective heating solution.
⭐ Factors to Consider When Choosing a Heating System
Choosing the best heating system for your home involves considering factors such as:
- cost
- comfort
- energy efficiency
- maintenance
- your specific home and climate needs
By balancing these factors and understanding the different types of heating systems available, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs.
An HVAC professional consultation can help identify your home's most suitable heating system, considering factors like installation costs, ongoing energy expenses, and potential rebates or tax credits for high-efficiency systems.
With the correct information and guidance, you can confidently choose the perfect heating system to keep your home warm and comfortable all year round.
⭐ Summary
In conclusion, various heating systems are available to suit every homeowner's needs and preferences. From traditional forced air systems to innovative solar-powered solutions, each type of heating system offers unique benefits and drawbacks.
By considering factors such as cost, comfort, energy efficiency, and maintenance, you can make an informed decision and select the perfect heating system for your home.
Remember, consulting with an HVAC professional can provide valuable insight and help you determine your home's most suitable heating system and climate.
With the right information and guidance, you can confidently choose the perfect heating system to keep your home warm and comfortable all year round.
⭐ Frequently Asked Questions
What are the four types of heating systems?
The four main types of heating systems include furnaces, boilers, heat pumps, and ductless mini-split systems. Each system works differently to provide warmth and comfort to the home.
What is the newest form of home heating?
The newest form of home heating is Heat Pump Heating Systems, which use a system similar to air conditioners to extract heat from the air and deliver it to the home.
What is a forced air heater?
A forced air heater uses air ducts and vents to distribute heated air throughout a home or commercial building. It relies on a plan, which is a connected unit with ducts and vents, to transfer heat from a single location. This system is also used for central air conditioning systems.
What is the most energy-efficient heating system?
Heat pumps and ductless mini-split systems are the most energy-efficient heating systems available, making them the ideal choice for anyone looking to reduce their energy consumption.
Scott Harding
Scott is the main author of DIY Home Comfort. He's also an experienced HVAC technician that enjoys home renovation and spending time with his family. You can find out more about him here.