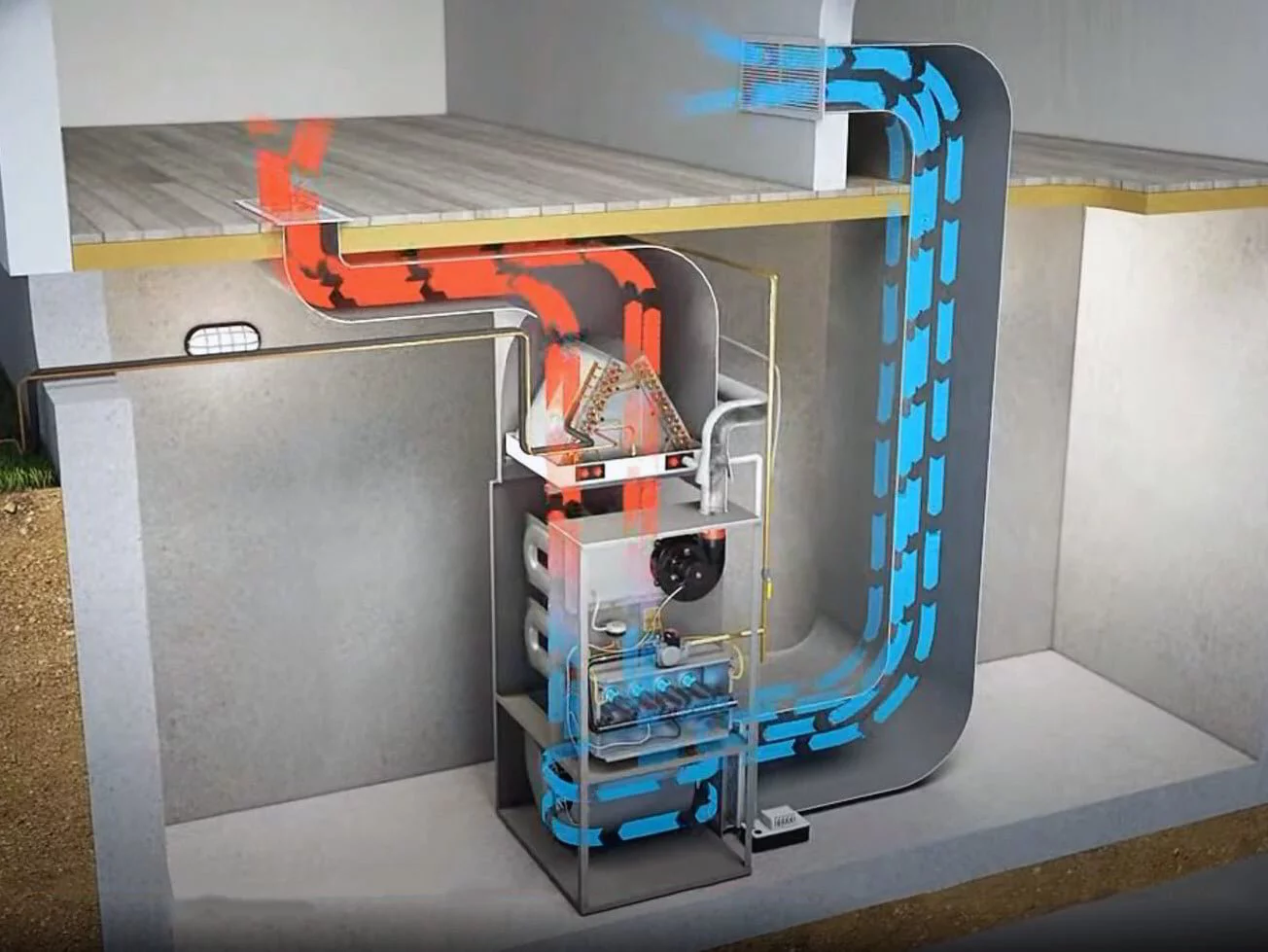
Heaters blowing cold air is a common yet perplexing issue for many homeowners, leading to discomfort and a pressing need for solutions. Understanding the causes of this problem is essential for effective resolution.
This article, authored by Scott Harding, a seasoned HVAC expert at DIY Home Comfort, delves into the nuances of home heating systems, offering insights into their mechanics and troubleshooting.
With his extensive experience in home heating, Scott provides reliable and practical information. Whether you're tackling the problem yourself or simply seeking to understand your home's heating system better, this guide offers valuable knowledge to ensure your space remains comfortably warm.
📘 Key Takeaways
- Understanding Heater Types: Different heaters (gas, electric, heat pumps) have unique mechanisms and common issues affecting their performance.
- Air Filter Maintenance: Regularly checking and replacing air filters is crucial for maintaining heater efficiency and preventing cold air problems.
- Pilot Light and Ignition Issues: For gas heaters, frequent pilot light outages or ignition failures often indicate a need for component cleaning or replacement.
- Ductwork and Gas Supply: Ensuring ductwork is leak-free and gas supply valves are functioning properly is essential for effective heating.
- Overheating and Safety Features: Recognize and address overheating issues promptly to prevent safety switches from triggering and causing the heater to blow cold air.
Understanding How Heaters Work
Heaters work by increasing the temperature of a space, providing essential comfort, especially in colder climates. The basic principle involves converting energy (from gas, electricity, or external heat sources) into heat and distributing this warmth throughout a space. The type of heater and its energy source significantly influence its operation and efficiency.
Gas Heaters:
- Operation: Use a pilot light to ignite gas in a combustion chamber.
- Air Circulation: A blower circulates the heated air through a heat exchanger.
- Common Issues: Pilot light malfunctions and gas supply challenges.
Electric Heaters:
- Operation: Generate heat through electrical resistance.
- Temperature Control: Thermostats regulate room temperature.
- Typical Problems: Heating element or thermostat malfunctions.
Heat Pumps:
- Operation: Transfer heat from the outside air or ground into the home in winter.
- Efficiency: Do not generate heat but move it.
- Potential Issues: Refrigerant level discrepancies and compressor problems.
Each type of heater operates uniquely, catering to different heating needs and preferences while also presenting specific maintenance requirements. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for proper heater selection, use, and maintenance.
📘 For more on the different types of heaters, check out: The Ultimate Guide to Different Types of Heating Systems
Common Causes of Heaters Blowing Cold Air
Thermostat Issues
Incorrect thermostat settings often result in heaters blowing cold air, especially if set to 'cool' or at a low temperature. Malfunctions such as dead batteries, sensor issues, or fuse problems also contribute to this issue, typically indicated by erratic heating or the heater not responding.
Modern smart thermostats, while convenient, can complicate matters with their advanced features like remote control and learning schedules, potentially leading to inadvertent missettings. Ensuring proper setup and understanding of these features is key to preventing thermostat-related heating issues.
Air Filter Problems
Clogged or dirty air filters significantly impair heater performance across all types. In gas heaters, restricted airflow can cause overheating and automatic shutdowns. Electric heaters may experience reduced efficiency and increased operating costs.
Heat pumps, relying heavily on airflow, can suffer from decreased heating effectiveness and increased strain on components.
Regular filter maintenance, such as monthly checks and timely replacements, is crucial. Emerging technologies like HEPA or washable electrostatic filters offer improved filtration, enhancing air quality and heater efficiency. Adopting these advanced filters can provide long-term benefits in maintaining optimal heater performance.
Pilot Light and Ignition Problems
Common issues with pilot lights in gas heaters include the light going out frequently or failing to ignite, often due to a dirty or faulty thermocouple, a clogged orifice, or problems with the gas supply.
In electric heaters, ignition problems typically stem from faulty ignition switches or sensors. For safety, always turn off the gas or power supply before troubleshooting. Innovative solutions include using self-diagnostic systems found in modern heaters, which can help identify issues with ignition components.
Smart diagnostic tools connected to mobile apps can provide real-time analysis and guidance for fixing these problems. Regular maintenance, including cleaning and inspecting these components, is essential for preventing ignition issues.
Ductwork Complications
Leaks or blockages in ductwork can significantly affect heating efficiency, leading to cold air distribution. In traditional duct systems, leaks often occur at joints and bends, while blockages are typically caused by accumulated debris.
Modern ductwork, designed for higher efficiency, can still face similar issues if not properly maintained. Regular inspections and sealing leaks with mastic or metal-backed tape can enhance efficiency.
Upgrading to insulated air ducts or implementing zoning systems in ductwork can further optimize heating performance, ensuring more consistent and energy-efficient delivery of warm air throughout the home.
Gas Supply and Valve Issues
Gas supply and valve issues in heaters can lead to insufficient heating or complete system failure. Common signs include the heater not igniting, producing a weak flame, or emitting unusual noises. These problems may stem from a closed valve, low gas pressure, or a faulty gas control valve.
Recent safety features in modern heaters include automatic shut-off systems and advanced valve controls to prevent gas leaks and enhance safety. Additionally, regulatory changes have emphasized using safer, more reliable valve mechanisms to ensure a consistent gas flow and reduce the risk of accidents.
Condensation and Drainage Issues
Condensation lines in heating systems, especially in high-efficiency furnaces and heat pumps, play a crucial role in removing condensation produced during heating. Clogs in these lines can lead to water backup and system malfunctions, inefficiencies, or even damage.
Innovative solutions for managing condensation include installing condensate pumps for better drainage and using environmentally friendly, non-corrosive cleaning agents to clear the lines, preventing buildup regularly.
Additionally, newer systems often feature advanced condensation management technologies, such as self-cleaning mechanisms, which help maintain optimal functionality while minimizing environmental impact.
📘 Related Reading: What is a Condensate Drain Line and Why It's Important
Overheating and Safety Features
Overheating in heating systems can trigger built-in safety features, leading to the system shutting down and consequently blowing cold air. This safety mechanism protects the system from damage and prevents potential fire hazards.
Overheating can occur due to various reasons, such as restricted airflow from clogged filters, mechanical failures, or excessive strain on the heating components. When the system overheats, the safety switch activates, halting operation until the issue is resolved.
Regular maintenance and prompt attention to any signs of overheating are crucial for the safe and efficient functioning of heating systems.
DIY Troubleshooting Steps
When facing common heater problems, there are several DIY troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Check the Thermostat: Ensure it's set to "heat" mode and the temperature is set higher than the room temperature. Replace batteries if it's battery-operated.
- Inspect Air Filters: A dirty or clogged air filter can restrict airflow, leading to overheating. Clean or replace them as necessary.
- Pilot Light and Ignition System: For gas heaters, check if the pilot light is lit and the gas valve is on. For electric heaters, ensure there are no issues with the ignition system. Use the heater’s manual for guidance on relighting or troubleshooting.
- Examine Circuit Breakers: Ensure the heater's circuit breaker hasn't tripped. If it has, reset it and monitor for recurring issues.
- Look at the Vents: Make sure all vents are open and unobstructed for proper airflow.
- Utilize Modern Tools: Many modern heaters have diagnostic LED lights or will display error codes. Refer to the manual for interpretation. Additionally, there are mobile apps available for some models that can assist in diagnostics and provide troubleshooting steps.
- Safety First: Always turn off the power to the heater before performing any checks or maintenance.
Remember, these steps are for basic issues. If the problem persists, it may be time to call a professional.
When to Call a Professional
Recognizing when to call a professional for HVAC issues is crucial. Key indicators include persistent problems despite troubleshooting, unusual noises from the heater, an unresponsive thermostat, and signs of gas leaks or electrical issues.
As HVAC technology evolves, professionals now offer services like smart home integration, energy efficiency audits, and eco-friendly solutions. When choosing a service provider, look for licensed and insured technicians with good reviews and a track record of reliability.
Also, consider those who stay updated with the latest HVAC trends and technologies, ensuring they can handle both traditional and modern systems effectively
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is pivotal for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of heating systems. As suggested by competitors, basic maintenance routines typically include regular cleaning or replacing of air filters, checking and cleaning of burners, and ensuring unobstructed vents.
However, advanced maintenance practices go a step further. They involve eco-friendly and cost-effective strategies such as using energy-efficient filters, implementing smart thermostats for better temperature control, and scheduling annual professional inspections to identify potential issues early on.
These advanced practices extend the heater's life and contribute to a more sustainable and economical operation. Staying on top of these maintenance tasks can prevent costly repairs and ensure your heating system operates at peak performance.
Conclusion
This article provides a thorough overview of heater operation and maintenance. It delves into the specifics of different heater types, including their distinct operational mechanisms, and addresses various common challenges.
These include thermostat malfunctions, dirty air filter issues, problems with pilot lights and ignition systems, ductwork complications, and troubles related to gas supply, valves, condensation, drainage, and overheating. Each aspect is explored in detail, offering a comprehensive understanding of what goes into maintaining a heating system efficiently and effectively.
DIY Home Comfort, with its in-depth expertise and extensive experience, provides high-quality information and practical advice on these topics. Readers seeking further insights and detailed guides on home heating systems are encouraged to explore other heating articles.
You will find a wealth of resources underpinned by thorough research and credible information to help you maintain an efficient, safe, and comfortable home environment.
Scott Harding
Scott is the main author of DIY Home Comfort. He's also an experienced HVAC technician that enjoys home renovation and spending time with his family. You can find out more about him here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my furnace blowing cold air instead of hot?
This problem can often be attributed to issues such as a malfunctioning thermostat, clogged air filters, gas supply problems, or a pilot light that's out. Regular maintenance and checking of these components can often resolve the issue.
What should I do if my heater's pilot light or ignition system malfunctions?
For gas heaters, check if the pilot light is lit or if there are any issues with the ignition system. Cleaning the pilot light area or relighting it as per the manufacturer's instructions can help. For ignition problems, consult the manual or a professional.
How can I address low refrigerant levels in my HVAC system?
Low refrigerant levels, often due to leaks or inadequate charging, can hinder the heating process. It's advisable to consult a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and fix these leaks, then recharge the system with the appropriate refrigerant level.
Can blocked vents or registers affect my heater's performance?
Yes, blocked vents or registers can lead to ineffective warm and cool air distribution. Ensuring that all vents and registers are open and unobstructed is crucial for the heating system to function properly.
How do clogged air filters impact the heating system?
Clogged air filters in heating systems restrict airflow, leading to overheating, particularly in the furnace's heat exchanger. This causes the system to blow cold air. Regular filter maintenance, as recommended by the manufacturer, can prevent these issues, ensuring efficient operation.